Biologics are effective treatment options for various chronic inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Despite their promising potential, research has highlighted variability in individual response and the emergence of drug resistance under certain conditions. Therapeutic drug monitoring empowers researchers to investigate drug levels, immune response, and treatment dynamics.
Immundiagnostik, Inc. offers the IDKmonitor® line of therapeutic drug monitoring ELISAs to help labs measure drug levels and anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). This article will explore the line of ELISAs and the biologics they measure.
The IDKmonitor® Drug level ELISAs are intended for the quantitative determination of active substance concentrations and to assess the bioavailability of the selected biologic.
The effectiveness of biologics largely depends on the serum concentration of the drug, as bioavailability and pharmacokinetics are individual and vary through the course of disease. Monitoring the drug level, especially the trough level, is therefore essential to ensure that the drug is sufficiently available in circulation and to adjust its dose if necessary. Additionally, a reduced trough level during therapy may indicate the presence of antibodies to the drug.
The IDKmonitor® Anti-drug Antibody (ADA) ELISAs are intended for the detection of ADAs and can provide information about the immune response to the respective biologic.
Treatment with biologics can lead to unwanted immune reactions if the body produces antibodies to the drug. This can cause allergic reactions, decreased efficacy, and therapy failure. Although adjunctive therapy with immunosuppressants can reduce ADA production, it is not always indicated. Monitoring ADA levels allows for early intervention, resulting in personalized, effective treatment with reduced side effects.
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) is one of the pro-inflammatory cytokines that promotes and maintains inflammatory responses. The protein is produced by macrophages and T cells and plays a central role in both acute and chronic inflammation. The TNFα concentration is greatly increased in many chronic inflammatory diseases (e.g. rheumatic diseases, Crohn’s disease) and affects the development and clinical course of these diseases. The overproduction of TNFα can be selectively inhibited by TNFα inhibitors (anti-TNFα antibodies).

The cell adhesion molecule α4β7-integrin is present on activated lymphocytes. By binding to MadCAM receptors, α4β7-integrin allows lymphocytes to migrate into the intestinal mucosa, promoting and maintaining inflammatory responses in the gut.

The binding of α4β7-integrin to MadCAM receptors can be selectively inhibited by α4β7-integrin inhibitors. Since MadCAM receptors are restricted to the gut, the effect of α4β7-integrin inhibitors is gut-specific.
α4β7 Drug: Vedolizumab
Interleukin-12 and 23 are cytokines that regulate the immune system and influence inflammatory responses triggered by immune activation.
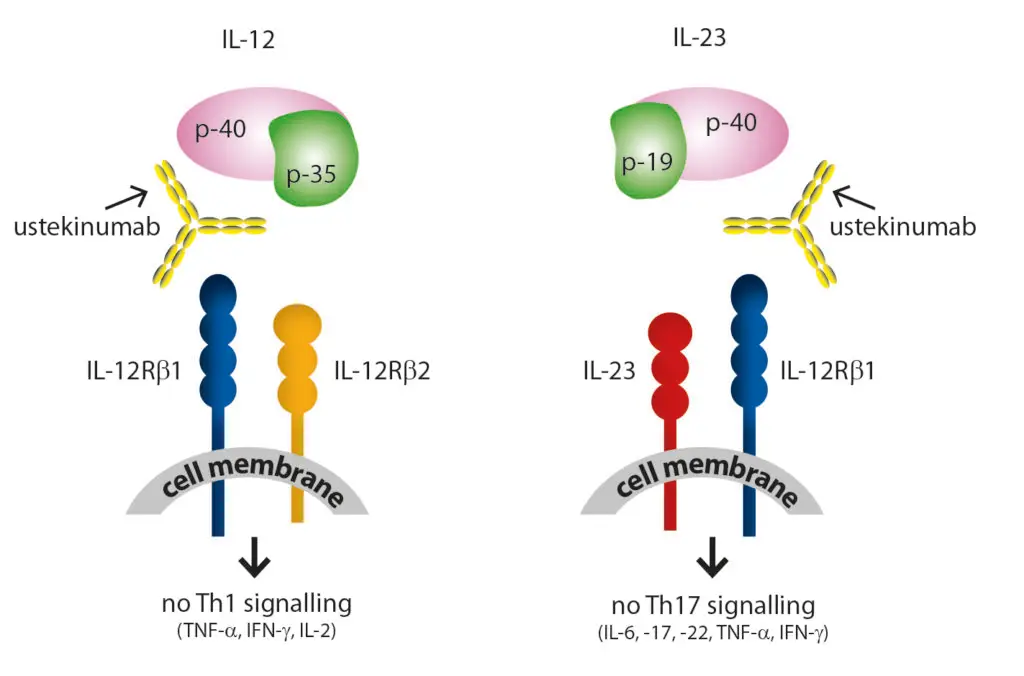
IL-12 stimulates the Th1 signaling pathway through cell membrane receptors, while IL-23 activates the Th17 signaling pathway. Both cytokines contribute to the maintenance of inflammatory reactions. IL-12/23 inhibitors target the shared subunit p40 of these cytokines, preventing their binding to their respective receptors. This inhibition blocks the inflammatory signaling cascade.
Drug: Ustekinumab
CD20 (also known as human B-lymphocyte-restricted differentiation antigen or Bp35) is a surface antigen found on normal and malignant pre-B lymphocytes as well as mature B lymphocytes. It plays a crucial role in optimizing the B cell immune response, particularly against T cell-independent antigens, and may also function as a calcium channel.

The CD20 antibody, through its binding to CD20, among other things, improves the action of natural killer (NK) cells, which cause cell death in antibody-labeled B lymphocytes. This process leads to cell death in the antibody-labeled B cells, significantly reducing their numbers. This reduction is a key goal in lymphoma therapy. In autoimmune diseases, lowering the number of B lymphocytes also decreases autoantibody production, thereby improving symptoms.
Drug: Rituximab
Free ADAs refer to antibodies that are not bound to the therapeutic antibody. This has technical implications; specifically, free antibodies can only be detected when the drug level is low or undetectable. Moreover, the presence of free ADAs indicates that the individual’s immune response is producing more ADA molecules than there are circulating drug molecules available.
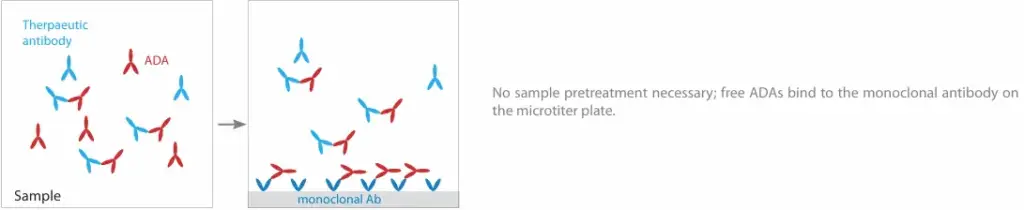
Free ADAs refer to antibodies that are not bound to the therapeutic antibody. This has technical implications; specifically, free antibodies can only be detected when the drug level is low or undetectable. Moreover, the presence of free ADAs indicates that the individual’s immune response is producing more ADA molecules than there are circulating drug molecules available.
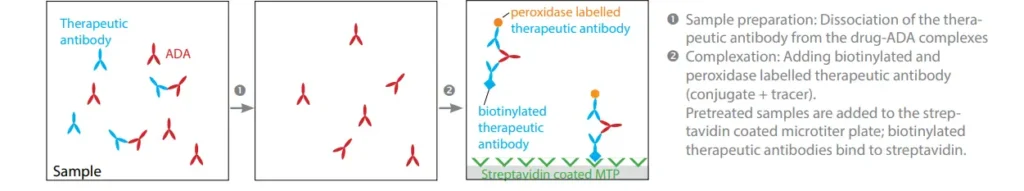
IDKmonitor® Therapeutic Drug Monitoring ELISAs can reliably measure both the original drugs as well as their biosimilars under WHO-compliance.
Target | Drug | Drug Level Sample Volume: 10 µL | Free ADA Sample Volume: 25-50 µL | Total ADA Sample Volume: 25 µL |
TNFα | Infliximab | |||
Adalimumab | ||||
Golimumab | – | |||
Etanercept | – | |||
Certolizumab | KR9662 | – | – | |
α4β7-Integrin | Vedolizumab | – | ||
IL-12/23 | Ustekinumab | KR9667 | ||
CD20 | Rituximab | KR9661 | Coming soon! | – |
The IDKmonitor® ELISAs are manufactured by Immundiagnostik AG.
*Health Canada Licensed.
All Other Products are For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
All Products are For Laboratory Professional Use Only.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.